Classical Period
The classical period in music lasted from about 1750-1820. This time period was one of freedom - of ordinary people questioning how society was organized and asserting their basic rights as citizens. American citizens won their independence from England in 1783, and the French public (who had assisted the United States during the American revolutionary war) decided they wanted the same type of freedom. In 1789 they stormed the Bastille and finally de-throned and be-headed their monarch, King Louis XVI in 1792.
The pace of technological change and innovation accelerated. The development of steam power and invention of mass production techniques started the Industrial Revolution.
The Rococo
The beginning of the period started with a refinement of the excesses of the Baroque period. The Rococo was a style that epitomized the grace, elegance and sophistication of courtly life. The word Rococo is seen as a combination of the French rocaille, or shell, and the Italian barocco, or Baroque style. Where the Baroque was gaudy and 'over-done', Rococo was more delicate; still ornate, but in a more graceful style. Rococo style began in the decorative arts and interior design - furniture, room decor, painting. The artisans and artists developed lighter elements with more curves and natural patterns, often asymmetrical (non-balanced).
Age of Enlightenment
By the end of the eighteenth century there was a reaction against the stylistic frivolities of the Rococo style and the type of society that produced it. The common man resented the excesses of courtly life and began to question the authority of Kings and government. They were looking for the simplicity and balance that had been evident in the ancient cultures of Greece and Rome. Archeological discoveries of Pompeii (a Roman city buried and preserved by volcanic ash) in 1748 might have have fueled the interest in ancient Roman culture and ideals. Often, the Classical Period is known as the neo-classical period (the new classical).
Historical Events
1759 Voltaire writes Candide
1774 Thomas Paine writes Common Sense
1775 Thomas Watts perfects the Steam Engine
1776 American Declaration of Independence
1789 French Revolution
1793 Eli Whitney patents the cotton gin
1804 Napoleon crowns himself Emperor of France
Art, Architecture and Literature
The Rococo art style appealed to the senses rather than intellect, stressing beauty over depth. The movement portrayed the life of the aristocracy, preferring themes of romance, mythology, fantasy, every day life to historical or religious subject matter. Rococo was a light, ornamental, and elaborate style of art, identified by elegant and detailed ornamentation and the use of curved, asymmetrical forms. Other elements of the style included graceful movement, playful use of line, and delicate coloring.
Neoclassical art was a severe and unemotional form of art based on the grandeur of ancient Greece and Rome. Neoclassicism was a return to the purity of the art forms of ancient Rome and Greece with elements of simplicity, idealism, unity and harmony. The neoclassical artists rebelled against the excesses of the French aristocracy and the Roman Catholic Church, and was used as a way to inspire the masses. The art portrayed principles such as courage, sacrifice, equality, liberty, and patriotism and exhibited strong contrasts of color, clear tones, and dramatic compositions designed to stimulate noble action.
Representative artists of the Rococo period are:
Antoine Watteau (1684- 1721)
François Boucher (1703-1770)
Neoclassical artists include:
Jacques-Louis David (1748-1825)
Antonio Canova [sculpture] (1757-1822)
David Roberts (1796-1864)

Thomas Jefferson Memorial -inside. Washington. DC |
|
Features of Neoclassical Architecture:
Click on the image to the left to view the Jefferson Memorial (Washington D.C.)
Drag with your mouse to move, + and - controls to zoom
Many of our US government buildings were built during this period, so The White House, The Jefferson Memorial and The U.S. Capital Building are all examples of Neoclassical Architecture.
|
The Age of Enlightenment was fueled by the writers of the time. Literature of France and America was instrumental in uniting the people to over throw the monarchies that governed them.
Voltaire (1694-1778) wrote essays on civil liberties and social reform
Thomas Paine (1737-1809) wrote the pamphlet "Common Sense", which convinced American colonists to seek independence from England
Thomas Jefferson (1743-1826) wrote the American Declaration of Independence "...all men are created equal, that they are endowed by their Creator with certain unalienable Rights, that among these are Life, Liberty and the pursuit of Happiness"
|
Assignment #1 - Classical Report
Be Careful! The term 'Classical Music" is one that has been given to ALL 'serious' music. This report should not be about "Classical Music", but only about the "Classical Style Period” (1750-1820).
Also! There is another time period called “Classical Antiquity” referring to ancient Greece and Rome (800 BC to 600 AD). The founding of Rome and the death of Alexander the Great are NOT from the Classical Music Era. Homer and Virgil are NOT authors during 1750-1820!
Create a presentation on the Classical Period. You may create this presentation in MS Word or PowerPoint, in a webpage, blog or wiki. You may use another application to create the project if you ask for and receive teacher approval PRIOR to submission.
Write a report about the Classical Style Period.
This report should NOT be about the music of the Classical Period, but rather the world events, painters &/or sculptors, authors and buildings of this time period.
The presentation should contain information about the following 4 areas:
History (World Events)
Art (Include famous artists of the period and an example of the their work)
Architecture (Describe the characteristics of the period, and include at least 1 example of the architectural style of the period)
Literature (Include famous authors of the period and an example of their work).
See the scoring rubric for expectations. 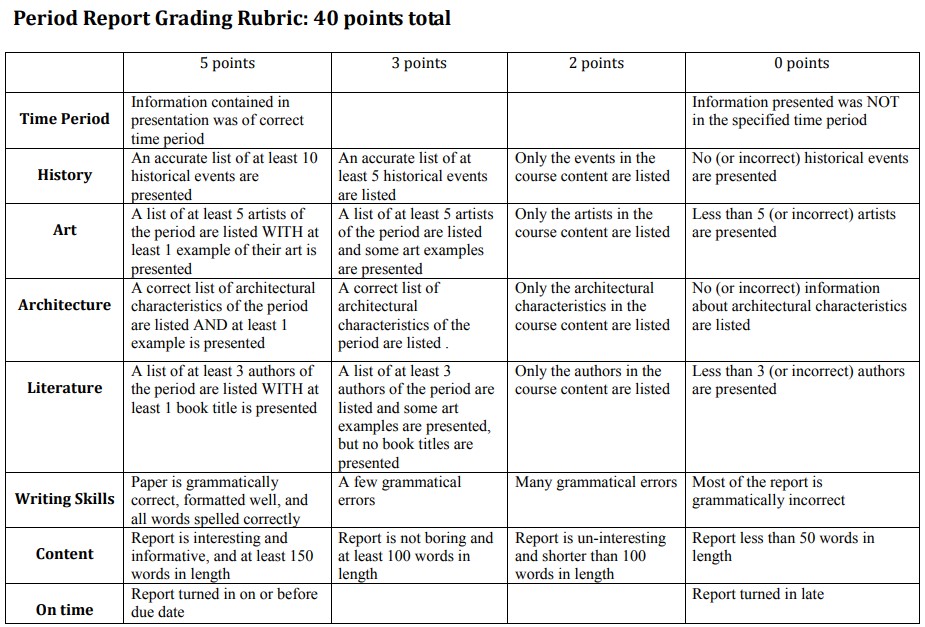
Click here to view a previous student example: 
|
Classical Music
When most people use the term 'classical music' they apply it to any music that is not in the popular culture of the time. Most people associate opera and symphonies with the words 'classical music'. Believe it or not, Gregorian Chant, opera, motets were all the popular music of the their time - that was the music that the people listened to. However, for our purposes here, we will consider classical music to be the music composed from about 1750-1820. The classical period is characterized by simplicity and restraint. The music of the classical period is planned, thought-out, well-ordered.
Homophony
In the Baroque period, most music was polyphonic - different voices, each with their own melody, combined together to form harmony. Classical composers focused their attention on the highest voice in the piece (the soprano singer in choral works, the trumpet or violin in instrumental). The melody would almost always be performed by that highest voice, while the other parts would fill in the harmony. The importance of the bass line (the basso continuo) of the Baroque largely disappeared during the Classical period. But the emergence of the obbligato accompaniment became prevalent. An obbligato accompaniment is a secondary voice (a second violin part, or cello, or tenor singer) that adds their own melody to the piece and although not the most important voice, it crucial to the piece of music.
Harmonic Rhythm
In the Baroque period, the harmony often changed beat by beat; in Classical music the harmony might remain the same for measures or several phrases of music. This is due to the fact that the melody (in the upper part) would usually be made up of notes that would fit in a particular harmony, and since the lower parts were only there to produce that harmony, there was no reason to change often. Composers started to think about music chordally, that is where the melody would be played over a chordal structure that defines the harmony of the piece. Much like a singer and guitar might perform a song today - the singer sings the melody, and the guitarist plays chords that accompany that melody. The actual position and voicing of the harmony is not all that important.



